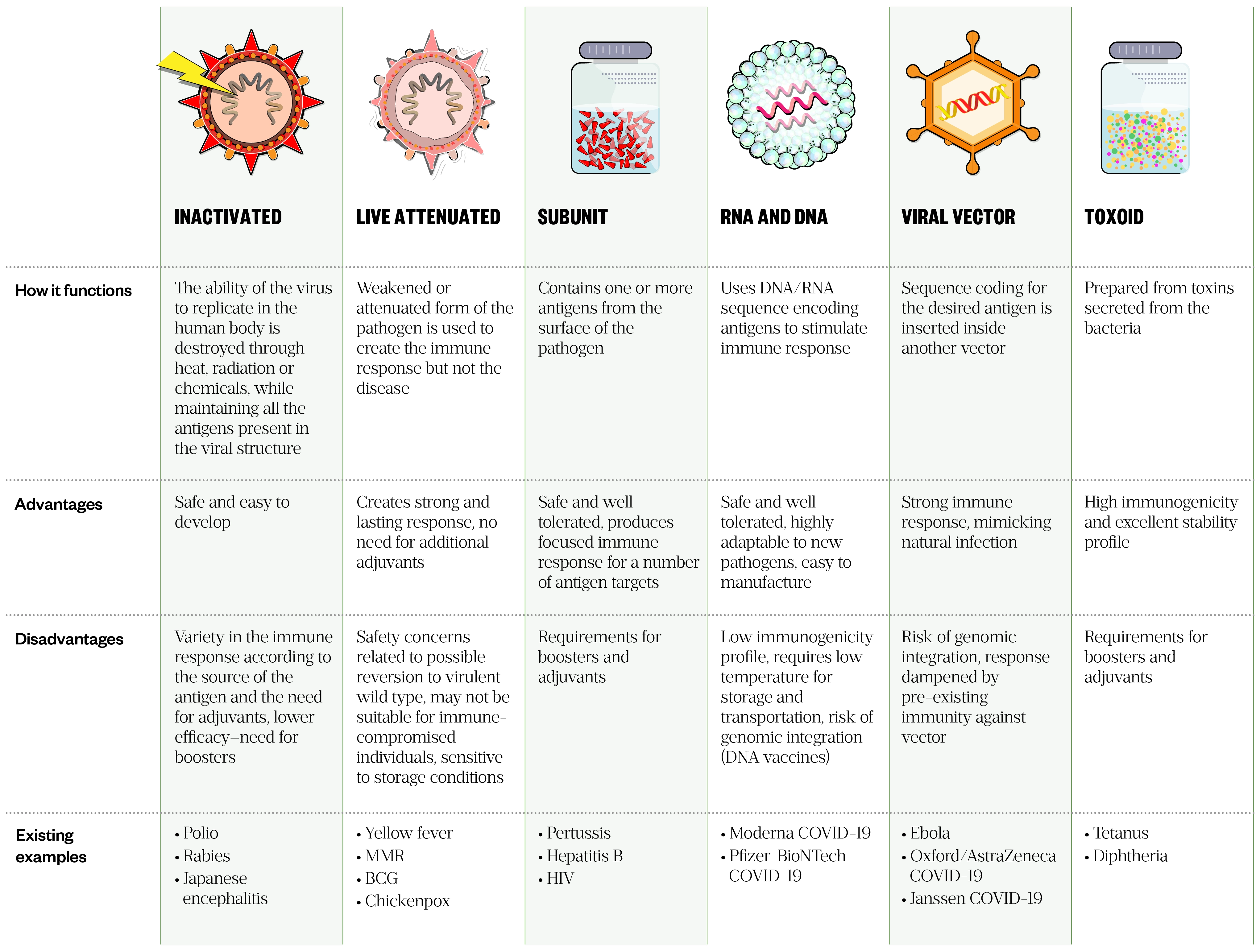
types of vaccine delivery system
Recent decades have brought major advances in understanding the complex interactions between the microbes. The system is produced by conjugation of polyleucine to peptide antigen followed by self-assembly of the conjugate into nanoparticles.

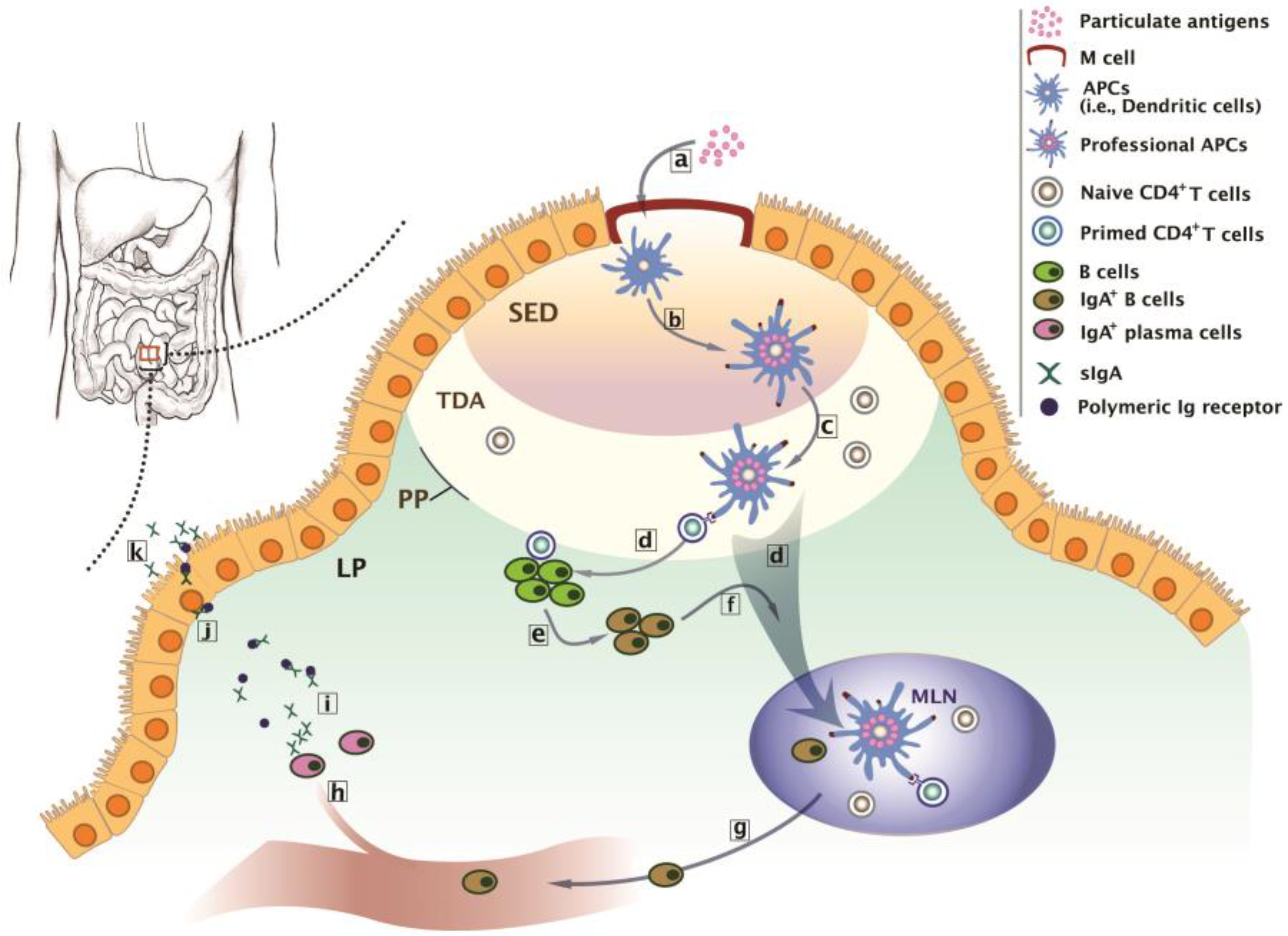
Polymers Free Full Text Oral Vaccine Delivery For Intestinal Immunity Biological Basis Barriers Delivery System And M Cell Targeting Html
Immunostimulatory adjuvantsConserved molecular patterns of.
. MAS-1 is an investigational low viscosity free-flowing water-in-oil emulsion-based adjuvantdelivery system comprised of stable nanoglobular aqueous droplets. Polio vaccine was the first oral vaccine to be developed. W Potential harm to individuals with compromised immune systems eg.
Polio IPV Hepatitis A. The results were very positive in that the ease of the vaccines increased. Examples of vaccine delivery systems include liposomes emulsions and microparticles.
This review discusses selected viral vector systems and plasmid DNA and provides an overview of their specific characteristics strengths and limitations. We will discuss each of these briefly in the following slides. With one exception distribution and delivery of COVID-19 vaccines and other routine vaccines are accomplished through a federal delivery system.
Miniaturizing the vaccine delivery system also reduces the burden on the so-called cold chain a baton race from manufacturing plant to patient arm through a series of special refrigerated trucks and shipping containers designed to keep vaccines at. Measles mumps rubella MMR combined vaccine Varicella chickenpox Influenza nasal spray Rotavirus. In order to induce an effective protective immunity these vaccines require boosting with agents called adjuvants.
Vaccines of this type on US. Messenger RNA mRNA vaccine. Messenger RNA mRNA vaccines.
Adjuvants may allow hemagglutinin HA dose-sparing with enhanced immunogenicity. These include weakened or inactivated vaccines viral vector vaccines protein-based vaccines and RNA and DNA vaccines. New developments in vaccine delivery systems will improve the efficiency of clinical trials in the near future.
This photo shows a r esponder at an. Vaccine suspension of weakened killed or fragmented microorganisms or toxins or other biological preparation such as those consisting of antibodies lymphocytes or messenger RNA mRNA that is administered primarily to prevent disease. 3 rows Delivery systems for mRNA vaccines can be divided into viral- and non-viral vector delivery.
Most vaccine delivery systems are particulate including nanoparticles microparticles or adjuvant-formulated proteins. In this Special Focus experts in the field describe recent innovations in the design evaluation and use of novel vaccine delivery devices and systems. More information for how COVID-19 vaccines get to you.
The features modes of viral entry and replication expression of heterologous proteins issues related to both. Types of vaccine and adverse reactions w Attenuated pathogens can revert to original form and cause disease. Here we proposed a self-adjuvanting delivery system that is fully defined biodegradable and non-toxic.
This type of vaccine uses genetically engineered mRNA to give your cells instructions for how to make the S protein found on the surface of the COVID-19 virus. IC31 and IC30 novel types of vaccine adjuvant based on peptide delivery systems Expert Rev Vaccines. There are several types of vaccines including.
Thus new adjuvants or self-adjuvanting vaccine delivery systems are required. Affiliation 1 Intercell AG Campus Vienna. Toxoid inactivated toxin Diphtheria tetanus part of DTaP combined immunization.
It is demonstrated that weakened or inactivated vaccines have functioned well because of having two required signals to stimulate the immune system. The use of microneedles to deliver particle-based vaccines is gaining importance because of the combined advantages of particulate vaccine and pain-free immunization. An mRNA vaccine or RNA vaccine is a novel type of vaccine which is composed of the nucleic acid RNA packaged within a vector such as lipid nanoparticles.
Among the COVID-19 vaccines are a number of RNA vaccines under development to combat the COVID-19 pandemic and some have been approved or have received emergency use authorization in some countries. The main types of COVID-19 vaccines currently available in the US. Recommended Childhood ages 0-6 Immunization Schedule.
Viral vectors have different capabilities as gene delivery vehicles for vaccines and immunotherapeutics. 10 rows A key advantage of liposomes archaeosomes and virosomes in general and liposome-based vaccine. Dime-sized patch of dissolvable microneedles for self-administration of influenza vaccine.
Among them nanoparticles NPs such as dendrimers polymeric NPs metallic NPs magnetic NPs and quantum dots have emerged as effective vaccine adjuvants for infectious diseases and cancer therapy. The antigen and the natural adjuvant. New influenza vaccines are needed to increase vaccine efficacy.
Pfizer distributes and delivers doses of its COVID-19 vaccine through its own delivery system. Concerted efforts by researchers on alternative vaccine delivery routes have yielded a range of novel delivery devices with potential to enhance immunogenicity and stability. Microneedle arrays are one example of a new method to deliver medications through the skin.
The vaccine antigens in the microneedles can be in solution or suspension form encapsulated in nano or microparticles and nucleic acid-based. In particular they describe novel polymeric. Vaccine delivery systemseg emulsions microparticles immune-stimulating complexes ISCOMs liposomes.
W Sustained infection BCG - local lymphadenitis. The size of the particle systems influences cellular targeting. Subunit recombinant polysaccharide and conjugate vaccines.
Latest vaccine delivery methods include use of oral vaccines. Scientific research has led to the development of numerous types of vaccines that safely elicit immune responses that protect against infection and researchers continue to investigate novel vaccine strategies for prevention of existing and emerging infectious diseases. Or being studied include.
After vaccination your muscle cells begin making the S protein. Authors Karen Lingnau 1 Karin Riedl Alexander von Gabain. Although nanoparticle delivery systems may improve the immunogenicity and pharmacokinetic efficacy of SUD vaccines SUD vaccines will likely need to be combined with standard medication-assisted.
Improving current delivery methods or designing new ones can enhance the use of existing medications. The common routes of vaccine delivery are parenteral injection needle-free injections intranasal ocular oral and spray topical.
Vaccine Advertising Preach To The Converted Or To The Unaware Npj Digital Medicine
Understanding Mrna Vaccine Technologies The Pharmaceutical Journal
How Pfizer S Mrna Coronavirus Vaccine Compares To Other Us Candidates
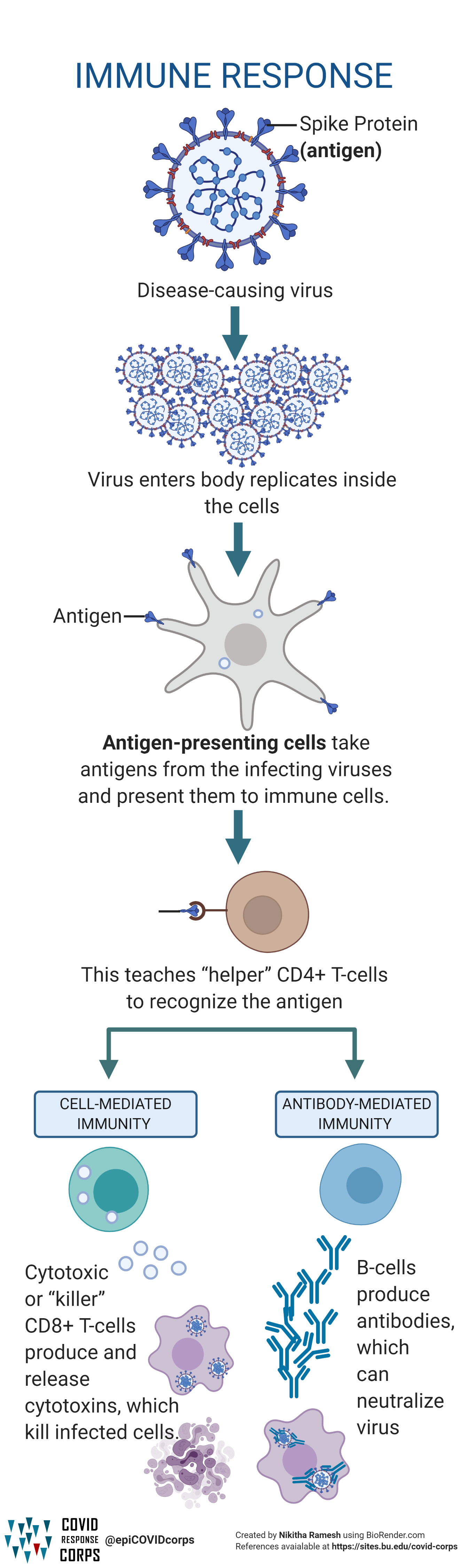
Types Of Vaccines Infographics Epidemiology Covid 19 Response Corps

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine

All Types Of Covid 19 Vaccines How They Work Animation Youtube

How The Sinovac Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times

Modes Of Action For Mucosal Vaccine Adjuvants Viral Immunology
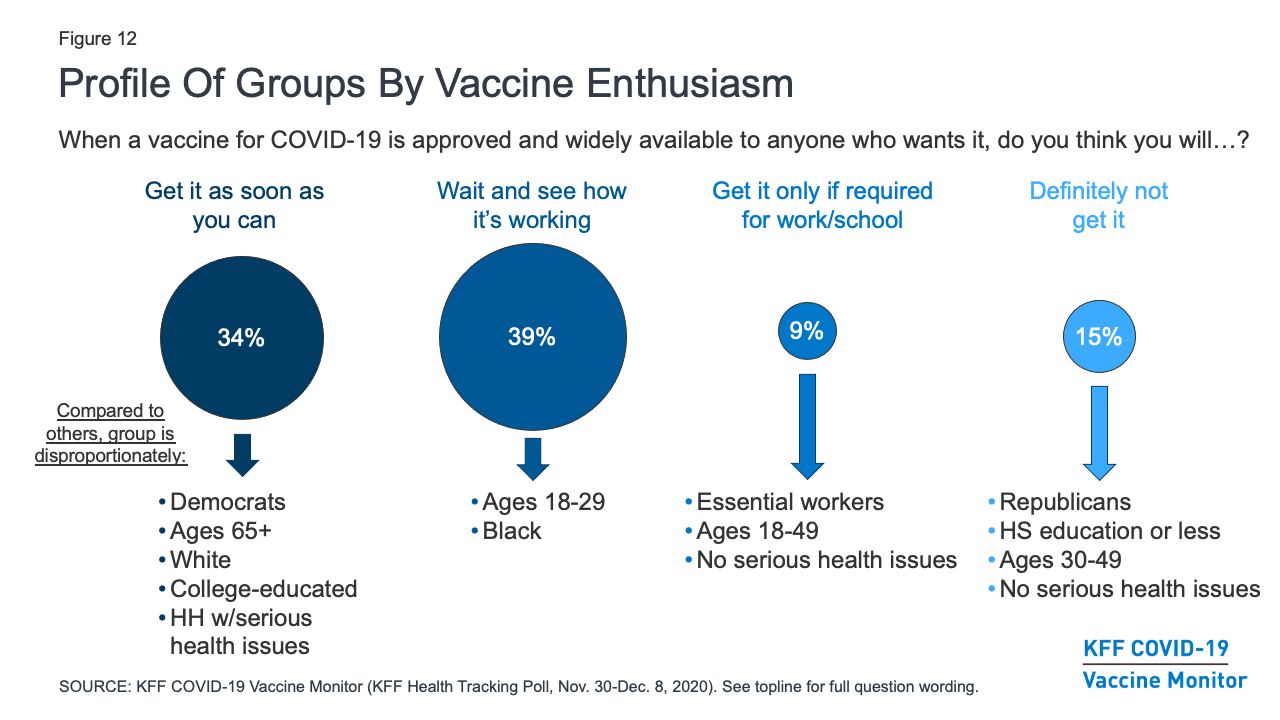
Kff Covid 19 Vaccine Monitor December 2020 Kff
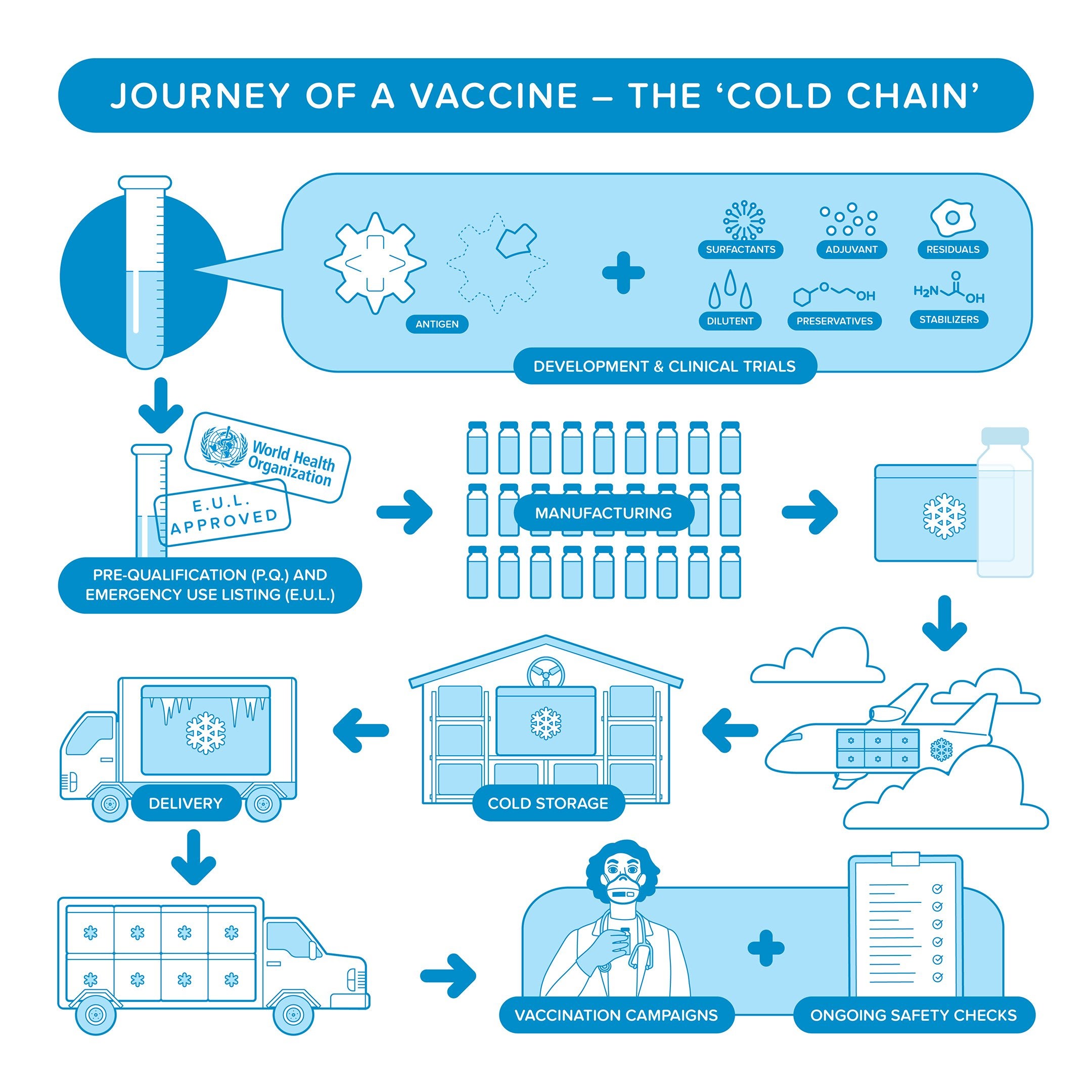
Cold Chain Paho Who Pan American Health Organization
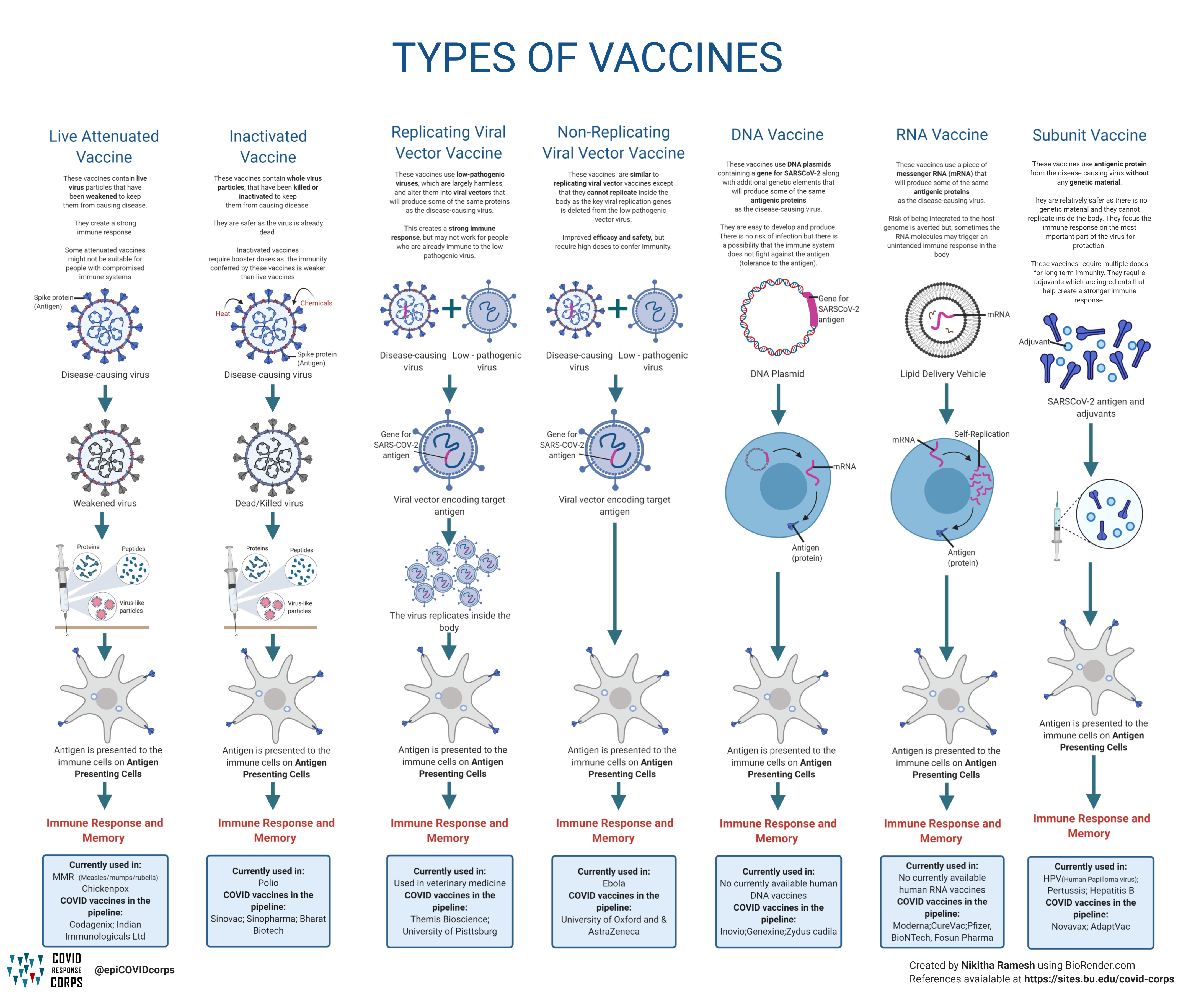
Types Of Vaccines Infographics Epidemiology Covid 19 Response Corps

How The Pfizer Biontech Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times
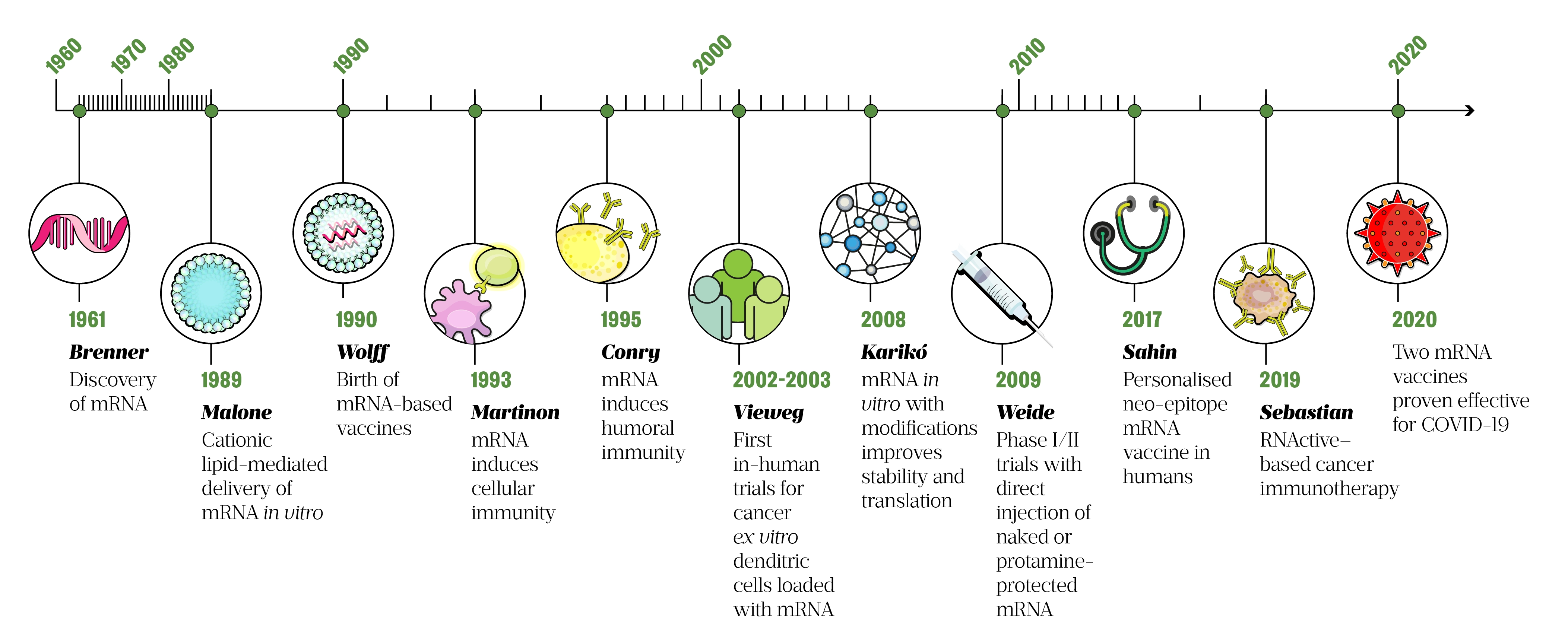
Understanding Mrna Vaccine Technologies The Pharmaceutical Journal

Prophylactic Vaccine Delivery Systems Against Epidemic Infectious Diseases Sciencedirect
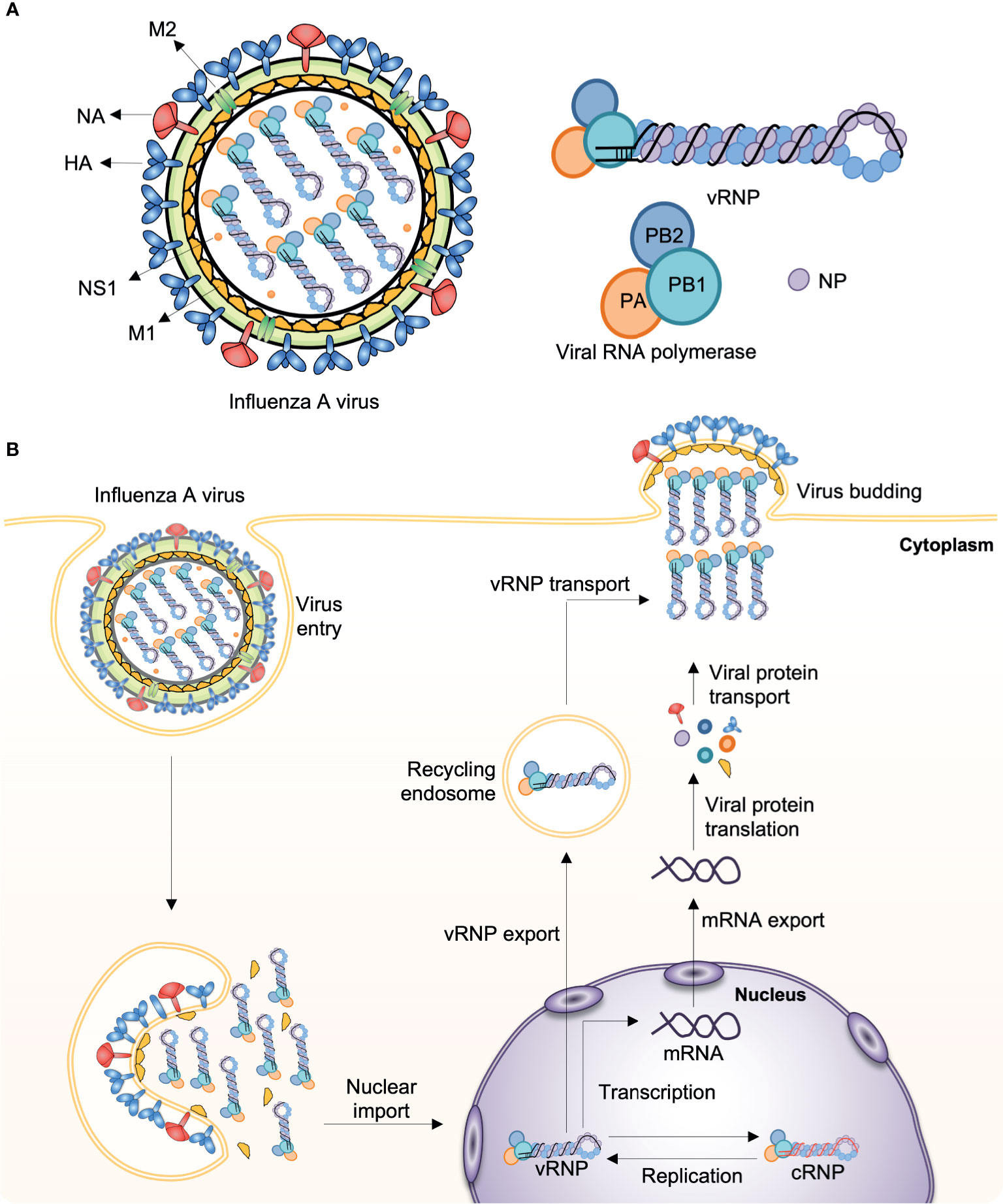
Frontiers Influenza Viruses Innate Immunity And Mrna Vaccines Immunology

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine

How The Pfizer Biontech Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times

Polymers Free Full Text Oral Vaccine Delivery For Intestinal Immunity Biological Basis Barriers Delivery System And M Cell Targeting Html